
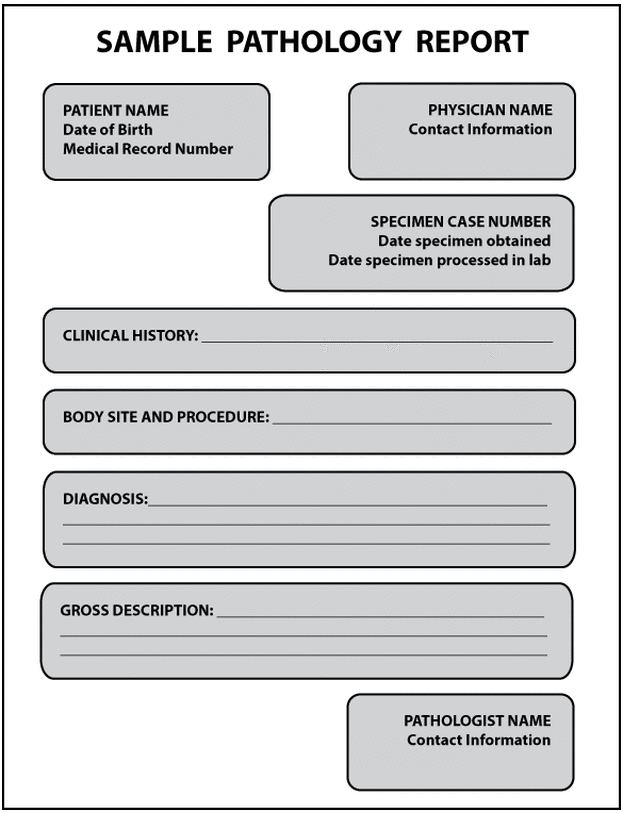
SEE ALSO: Getting a Second Opinion on Adrenal Cancer If there are any doubts about a diagnosis, the case will be reviewed with another pathologist. Then, the resident reviews the case with a pathology fellow and an attending pathologist. First, a pathology resident reviews the slides. Here at the U-M Rogel Cancer Center, each breast biopsy is reviewed several times. Kleer: I think second opinions are always worthwhile. Should patients get a second opinion on their pathology results? This personalized medicine approach requires a team of physicians of different specialties including clinicians and pathologists. Some patients have their tumors sequenced to find specific mutations that can be targeted with available medicines. The Cancer Center and the Department of Pathology has uniquely qualified specialists to perform genetic testing. Kleer: If genetic testing is indicated, based on the particular disease, this information is included in a special genetic report. What genetic information might be included on a pathology report? Thus, it is important to discuss all diagnoses with your primary doctor. Pathology reports contain medical and scientific terms that may be difficult for nonmedical people to understand. Kleer: Once the pathologist writes a report, the physician caring for the patient will communicate the results and explain the meaning of the diagnosis rendered, which will lead to a treatment plan. How does a patient interpret and understand the results of a pathology report? For example, finding cellular atypia and multiple division figures (or mitosis) may indicate that the tumor is growing rapidly, and guides oncologists and surgeons on the most appropriate treatment course. The pathologist can also perform additional tests on the tissues that can inform on the rate of growth and how the disease may evolve. The aim of the report is to provide the clinicians and surgeons with the necessary information so they can make a treatment recommendation. Kleer: The pathology report states as precisely as possible the disease present in the tissue sample. What information might a health care provider learn about a patient’s cancer from such a report? Be sure to ask questions if there are medical terms or details you don’t understand. Hormonal receptors will be performed.Īll of this information will be explained to you by your oncologist. See Comment.Ĭomment: The foci of ductal carcinoma in situ have focal necrosis and marked nuclear pleomorphism. Ductal carcinoma in situ extends to margins. In addition, there are multiple gritty yellow areas surrounding the nodule, measuring approximately 0.5 cm.ĭiagnosis: Left breast, excisional biopsy: High nuclear grade ductal carcinoma in situ with microcalcifications surrounding a fibroadenoma. The nodule is sectioned and submitted entirely for review. Gross description: A 3x2x2 cm oval fragment of fibrous and adipose tissue is received fresh and labeled “left breast biopsy.” Upon sectioning, there is a 1 cm tan firm nodule with a glistening surface. Here is an example of a breast biopsy diagnosis: The pathology report also has a section labeled “comments,” where the pathologist may note special features or unusual aspects of the sample. Under the diagnosis heading is a statement of whether the lesion excised is benign or malignant, and the specific medical term used to categorize the abnormal findings. This consists of the features of the tissue or organ seen with the naked eye, before study under the microscope. The report contains a macroscopic (also called gross) description of the tissue sample. Kleer: Each report has patient identifiers, including the name, birthdate, date of procedure and an assigned pathology accession number.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
